Dried Blood Spot Sampling
In a nutshell
What is Dried Blood Spot Sampling?
-
Easy way of collecting, shipping and storing blood samples
-
Simplifies the blood collection process and significantly reduces the costs involved
Dried Blood Spot Sampling (DBS) has been known for more than five decades. In recent years the usage of DBS has gained increasing importance since this method shows strong advantages compared to the conventional collection and analysis of blood or plasma samples. These advantages include the need for remarkably lower blood volumes and easier shipping and storage, mainly at ambient temperatures.


Streamlining Blood Sample Analysis
The blood sample needs to be extracted from the DBS card prior to the analysis. This was a major drawback of DBS previously. Sample extraction from a high number of DBS cards was very tedious and required many process steps to be performed manually. Hence, analysis of DBS was time-consuming and costly before the introduction of the CAMAG DBS-MS 500 instrument. The DBS-MS 500 enables fully automated sample recognition, integration of an internal standard to the DBS and direct sample extraction of the DBS from the card. The extract is guided online to an analytical system of choice (i.e. MS, LC-MS), and the system is cleaned after each extraction to prevent cross-contamination.
expanding applications of dbs technology
A typical field of application is newborn screening (NBS), where only a very small amount of blood from the newborn is available. Every newborn in developed countries is screened for inborn disorders via DBS.
Samples can be shipped to centralized laboratories for analysis via the standard mail delivery.
-
Reduction of test animals in preclinical studies due to lower blood volumes
-
Compliance with the 3R requirement of animal studies (replacement, reduction, refinement)
-
Personalized healthcare analysis of metabolites via automated DBS analysis is more affordable for the end-user and represents a growing market.
-
Testing of possible abuse of regulated substances is performed via DBS as well
Other body fluids
Dried Urine Spot
Urine is a biological fluid that is readily collectable and available. The shipment of urine samples is inconvenient. The sample preparation is tedious and requires many consumables. Dried Urine Spot (DUS) cards can easily be shipped and are integrated into the fully automated analysis concept for the DBS-MS 500. The urine matrix has been extensively researched and tested, and the technology has been in place for years. Quantification of targets in DUS can be facilitated by using creatinine as a marker for the urine concentration. Specific metabolites present in urine reflect a previous drug uptake for a period of hours to a few days.
Dried Plasma Spot
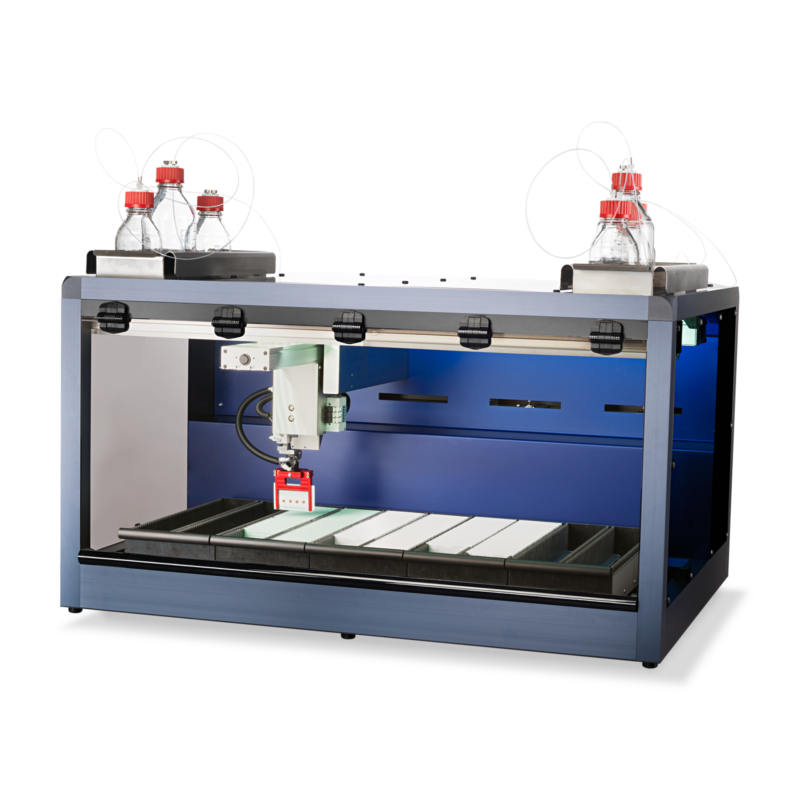
CAMAG® DBS-MS 500 HCT
-
High-throughput analysis of up to 500 DBS cards per run
-
Automated internal standard application module
-
Online coupling to the analytical system (MS or LC-MS)
Application fields
Application notes
FAQ
Are there commercial reagent kits available?
This depends on the field of application, please contact dbs@camag.com for detailed information.
Which reference laboratories exist?
NBS: R. Fingerhut, Childrens Hospital Zürich, SwitzerlandTDM: U. Duthaler, University Basel, SwitzerlandForensic: W. Weinmann, University Bern, SwitzerlandHaematocrit Research: C. Stove, University Ghent, Belgium
Which DBS or DMS cards can I use?
The gripper of the DBS-MS 500 is constructed to handle any cards that share the same format as 903, 226 or TFN cards. 84.67 mm × 53.2 mm (w × h).
What sensitivity is required?
This strongly depends on the target molecule concentration, please contact a CAMAG scientist for support.
Which LC-MS brand is compatible with the DBS-MS 500?
The DBS-MS 500 can be run with all common LC-MS brands. The Chronos software communicates with Shimadzu (Labsolutions), Agilent (MassHunter, Chemstation, EZChrom), Sciex (Analyst), Waters (MassLynx), Brucker (PACER) and Thermo (Xcalibur, QuanLab Forms).
How does the DBS-MS 500 communicate with the MS?
The communication is managed via the master Chronos software, which controls all systems. The DBS-MS 500 also communicates with any external device through an Ethernet connection, which is able to give “start”, “contact” or “closure” signals.
Is there a possibility to run the system under UPLC conditions?
Yes, the system comes with UPLC parts.
What are the system’s dimensions?
The DBS-MS 500 size is 110 × 80 × 60 cm (w × d × h). Additional space of 10 cm for ventilation and height of 30 cm for solvent bottle placement should be kept in mind.
How does the DBS-MS 500 system solve the problem of carry-over?
After each extraction, a designated wash station cleans all parts which were in contact with the DBS card. Studies have shown that there is absolutely no carry-over with this specially designed rinsing system.
How is the extraction process and analyte recovery in the DBS-MS 500 optimized?
The specially designed extraction unit allows perfect sealing of the extraction area and prevents solvent leaks. The extraction time, the solvent volume and its flow can be adjusted manually. The method optimization can be performed according to standard methods (educated guess) or an optimization protocol, which was developed by CAMAG.
What is the size of the extraction area?
The standard extraction head has a 4 mm diameter.
How is the internal standard (IS) applied to the sample?
The internal standard (IS) is applied through the integrated precision spraying device prior to extraction. Different drying times can be chosen within the Chronos software. The introduction of the IS to the sample just before the extraction enables the compensation of analyte recovery by creating the most similar processing conditions for both analyte and IS.
What is the recommended solvent for the internal standard?
It is recommended to use a solvent that dries relatively fast (e.g. methanol) to ensure that the sample is dry prior to extraction.
What is the price range of the DBS-MS system?
Please contact our sales department at sales@camag.com for detailed information on pricing.
How is the patient data recognized and linked with the report?
The optical card recognition unit (OCR) scans the barcode of each card prior to extraction and saves the information together with the analysis results.




